Introduction
This blog was funded by Bikeability and is also published on their website. Reproduced here with permission.
Download a Word version of this blog
Download a pdf version of this blog
E-assist can make cycling possible, or practical and comfortable, when it would otherwise be too tiring, sweaty, intimidating, or slow.
There are different kinds of e-assist which feel very different to use: Try a range of e-cycles to see which you prefer.
Choose your cycle type:
Check out our Top Tips: Choosing an accessible cycle part 1 – fit and function and Top Tips: Choosing an Accessible Cycle part 2 – cost, storage and more guides for more useful ideas.
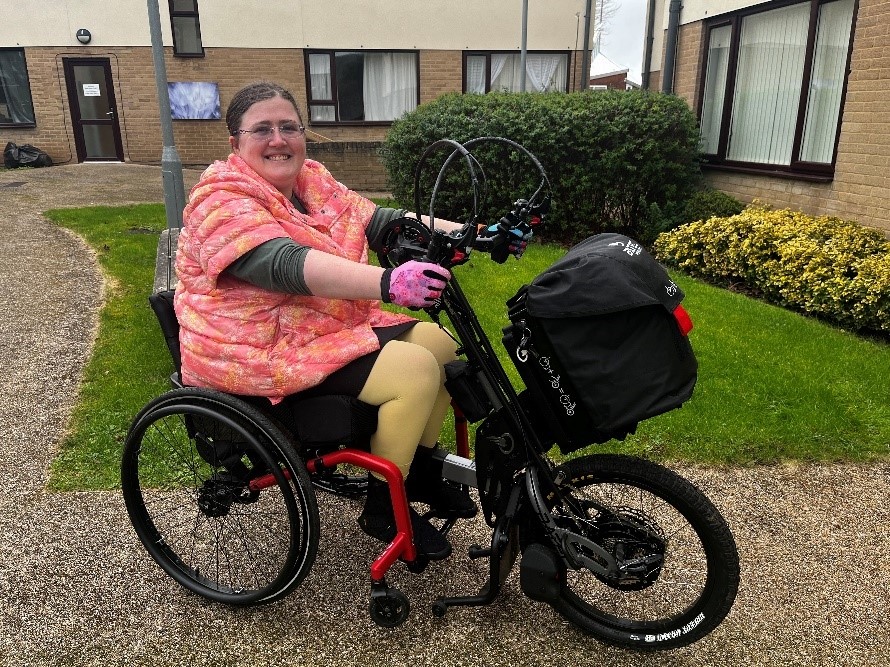

E-assist can make handcycling a great transport option
Choose a motor position
E-cycle motors can fit into a wheel (“hub motor”) or below the pedal crank (“mid motor”).
Hub motors:
- Usually cheaper than mid motors – found on many e-cycles, including handcycles and conversion kits.
- Provide power directly to the front or rear wheel – can feel strange to ride at first.
- Can prevent cycle having hub gears or hub dynamo lights.
Mid motors:
- Usually more expensive than hub motors. Major brands like Bosch and Shimano make mid-motors.
- Power added where you pedal – can feel more intuitive to ride.
- Can wear out cycle chains faster than hub motors.
Sensor types
E-cycle sensors switch the motor on when you’re pedaling.
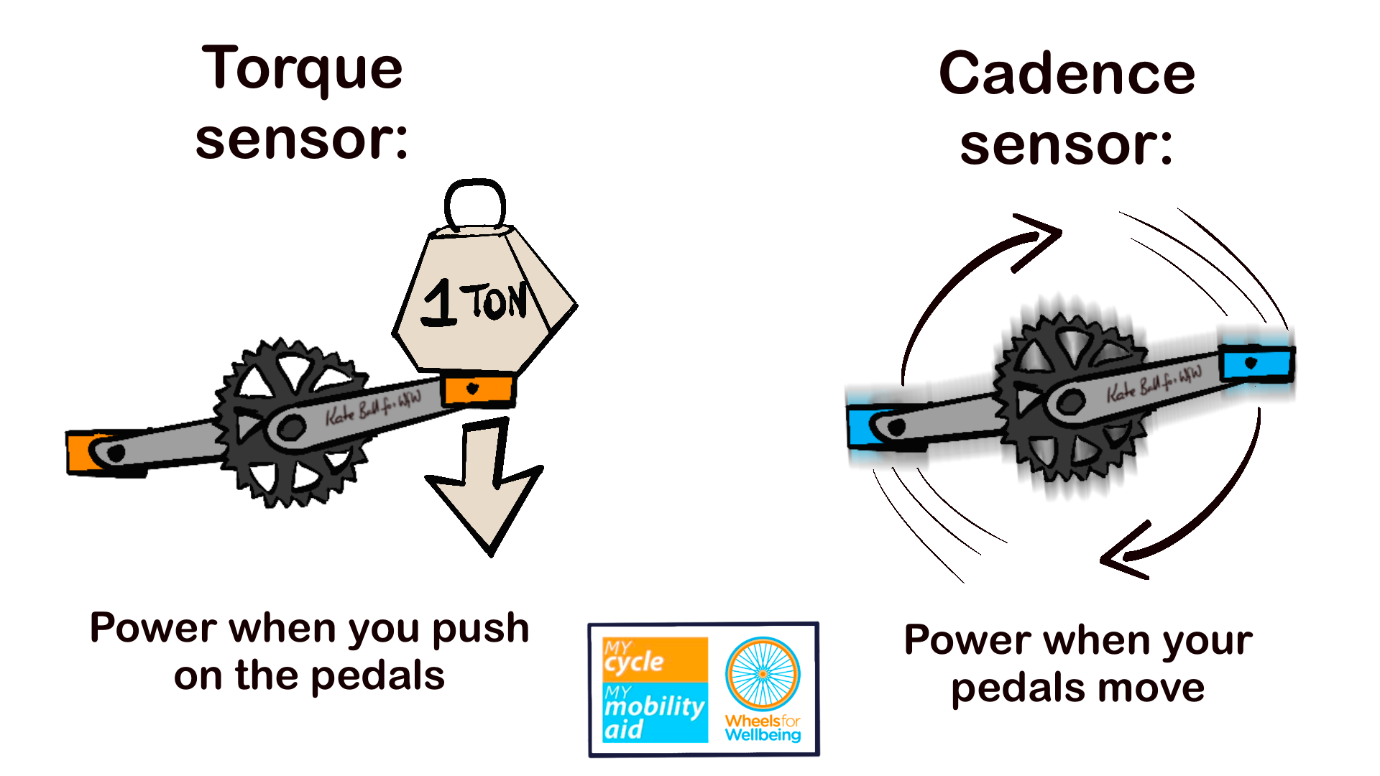
Torque sensors:
- Give power depending how hard you push on the pedals.
- Feel more “natural” when cycling
- Are usually fitted with mid-motors
- Some have “turbo” options to make starting easier.
Cadence sensors
- Switch the motor on when you move the pedals.
- Often only have one motor assist level per power setting
- Riding may feel less “natural” than with torque sensors with lag time starting and stopping the motor and power levels not matched with your effort
- Motor may use battery faster than with torque sensor
- Can be more difficult to move away from junctions due to slower start times.
Batteries
Capacity
Make sure your e-assist range will be enough for your rides: Check your battery’s predicted range and find reviews of real-world testing before you buy.
Remember that your battery’s maximum capacity will drop as the battery gets older and in cold weather.
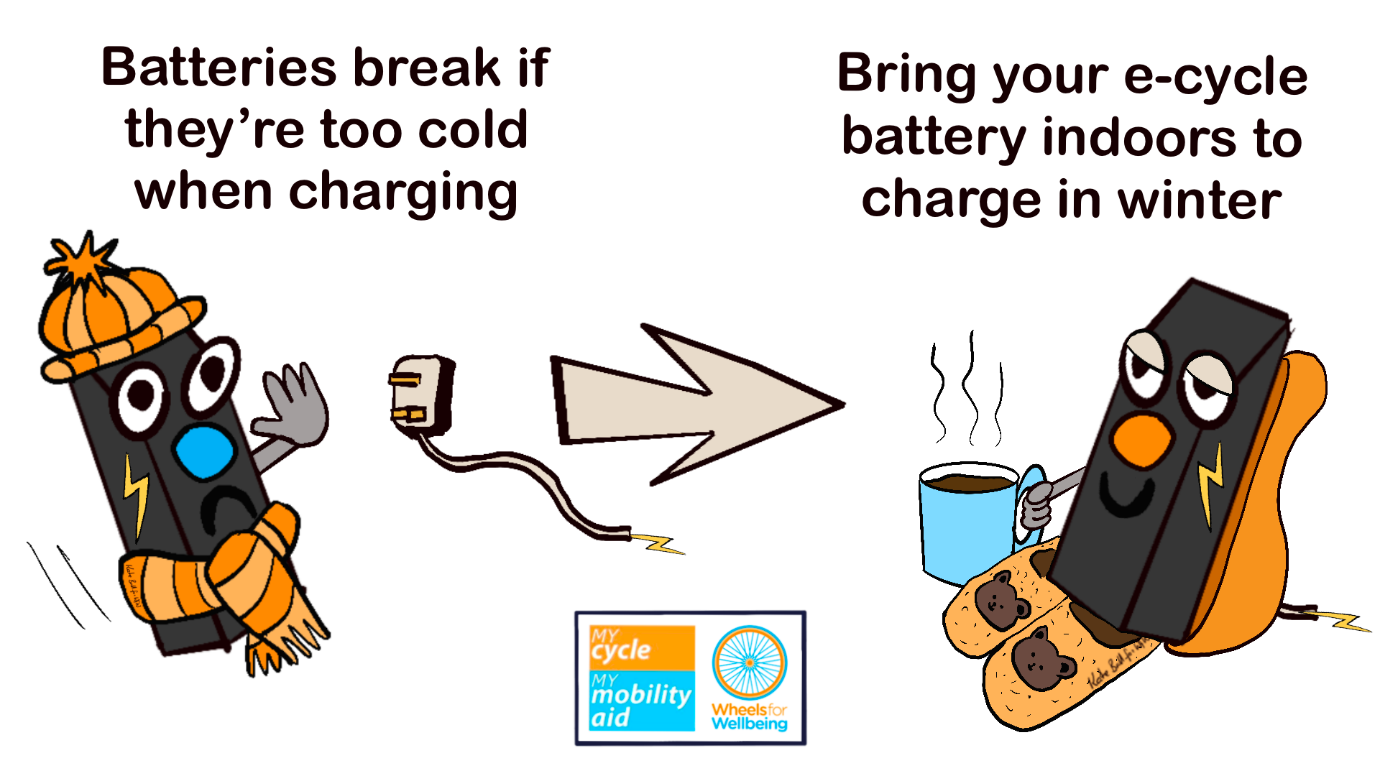
Charging
Batteries cannot charge in cold temperatures. There may be a fire risk, and it either just won’t work or you’ll permanently damage the battery.
You will need to bring your battery indoors to warm up for charging in winter.
If you can’t bring your whole cycle indoors, make sure the cycle you choose has a battery you can remove easily and carry inside.
Always follow the instructions to charge your e-cycle battery safely.
Purpose-built e-cycle or e-conversion?
Do you have a cycle you really love, but need a bit of extra power?
An e-conversion kit could be just the thing for you: https://ebiketips.road.cc/content/advice/buyers-guide/best-e-bike-conversion-kits
Consider durability, range and cycle compatibility for conversion kits.
The conversions we’ve seen use hub motors with cadence sensors, so if you want a mid-motor or torque sensor, conversions may not be an option.
Finally, before you buy make sure it’s legal
If you buy from a reputable cycle store, your e-cycle will be legal. If you’re buying parts to build an e-cycle yourself, stick to these rules so you don’t build an illegal motorbike by mistake!
You need to be aged 14 or over to ride an e-cycle. Legal e-cycles have:
- 5mph (25kph) max e-assist speed. You can pedal to go faster– but there will be no power from the motor;
- Must be pedaling for e-assist (unless the cycle is specifically type rated and certified);
- 250 watt maximum motor.
There are grey legal areas around throttles (moving without pedaling like an e-scooter or mobility scooter) up to walking speed and on adaptive cycles designed specifically for Disabled users. Higher speed throttles on standard bikes are definitely not allowed unless the cycle has been individually type rated (certified).
Throttle assist can be a game-changer for Disabled riders especially, so clarity around allowing throttles for Disabled people would make a big difference to many people.
Wheels for Wellbeing are campaigning for similar rules to apply to e-cycles, escooters, mobility scooter, powerchair and other micromobility devices. Find out more and add your voice via our Twitter, Facebook, @Wheels4Well and website www.wheelsforwellbeing.org.uk
About us
Wheels for Wellbeing is a Disabled People’s Organisation working to make cycling, wheeling and walking accessible for everyone.
Blog author Kate Ball is a Disabled cyclist, parent, carer and a Campaigns and Policy Officer at Wheels for Wellbeing. Her favourite cycle is a Circe Helios tandem which is really her daughter’s – but which all the family love to ride.
Useful organisations:
Wheels for Wellbeing: https://wheelsforwellbeing.org.uk/
Wheels for All: https://wheelsforall.org.uk/
Get Cycling: https://www.getcycling.org.uk/
Cycling UK: https://www.cyclinguk.org/
Sustrans: https://www.sustrans.org.uk/
Lifecycle: https://www.lifecycleuk.org.uk/
