This sheet is to aid discussion in accessible design for Disabled people walking/wheeling, cycling, using public transport & private vehicles
Download “Thinking about bus stop bypasses” in png format
Download “Thinking about bus stop bypasses” in docx format
Download “Thinking about bus stop bypasses” in pdf format
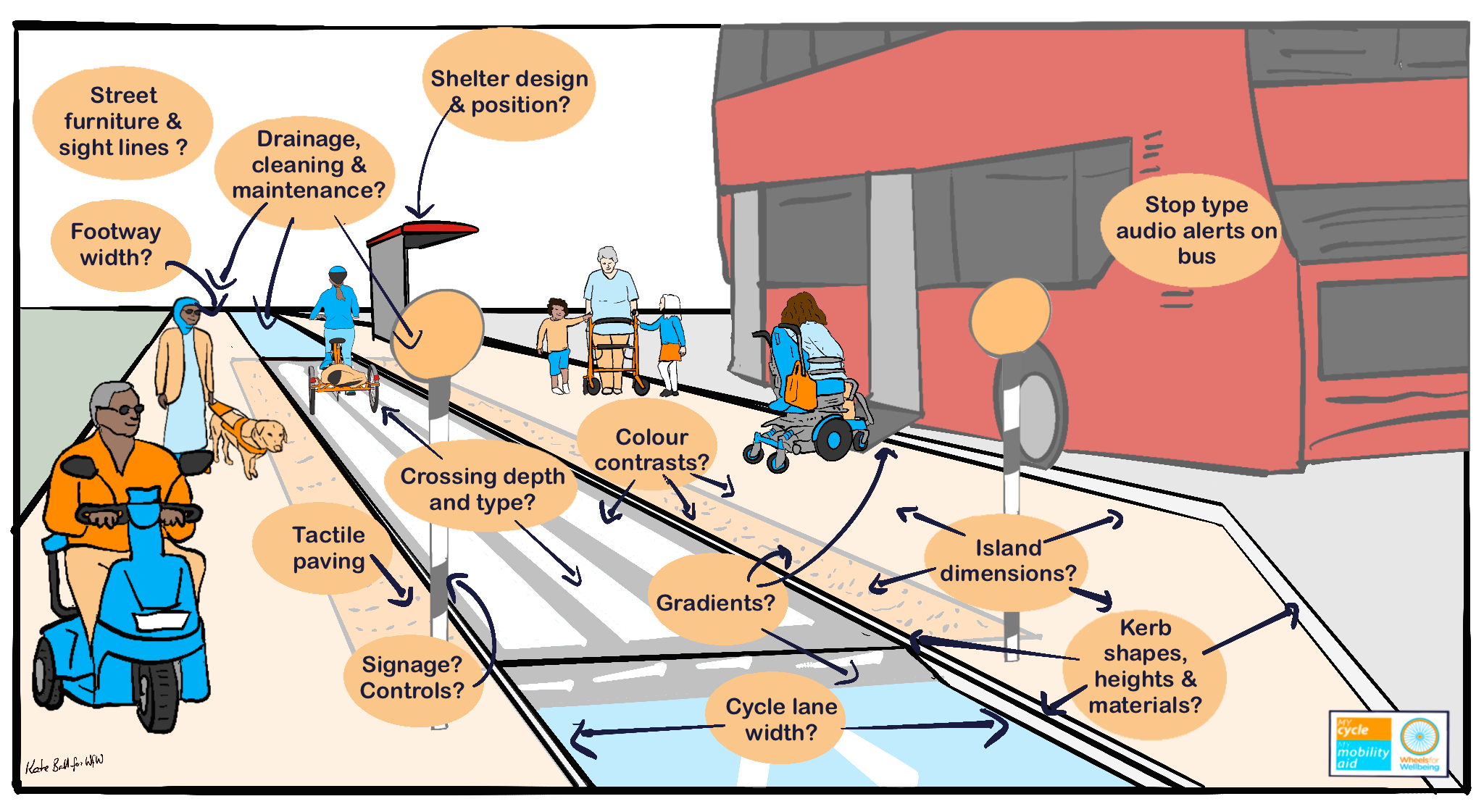
Bus stop bypasses – key points
Also known as floating bus stops. Installed on roads with cycle lanes. Continuous protected cycle lanes are required where carriageways are unsafe for inclusive cycling. IF a bus stop bypass is being considered:
- Bus stop island must be wide enough for all Disabled people to manoeuvre safely, including on & off bus ramp & through shelters;
- Step-free accessible crossing must be big enough to allow flexible desire line movement for bus users, & must require cyclists to give way;
- Kerbs other than at crossing points must be detectable (>60mm);
- Clear sight lines and space to road junctions are needed so cyclists can give way to pedestrians;
- Cycle lane widths, gradients, turns and kerbs must be accessible for Disabled cyclists, including those using non-standard cycles.
This is a discussion sheet, and does not imply support for any specific infrastructure design or category of designs. Wheels for Wellbeing call for inclusive consultation with Disabled people to ensure public space designs are accessible for everyone.
